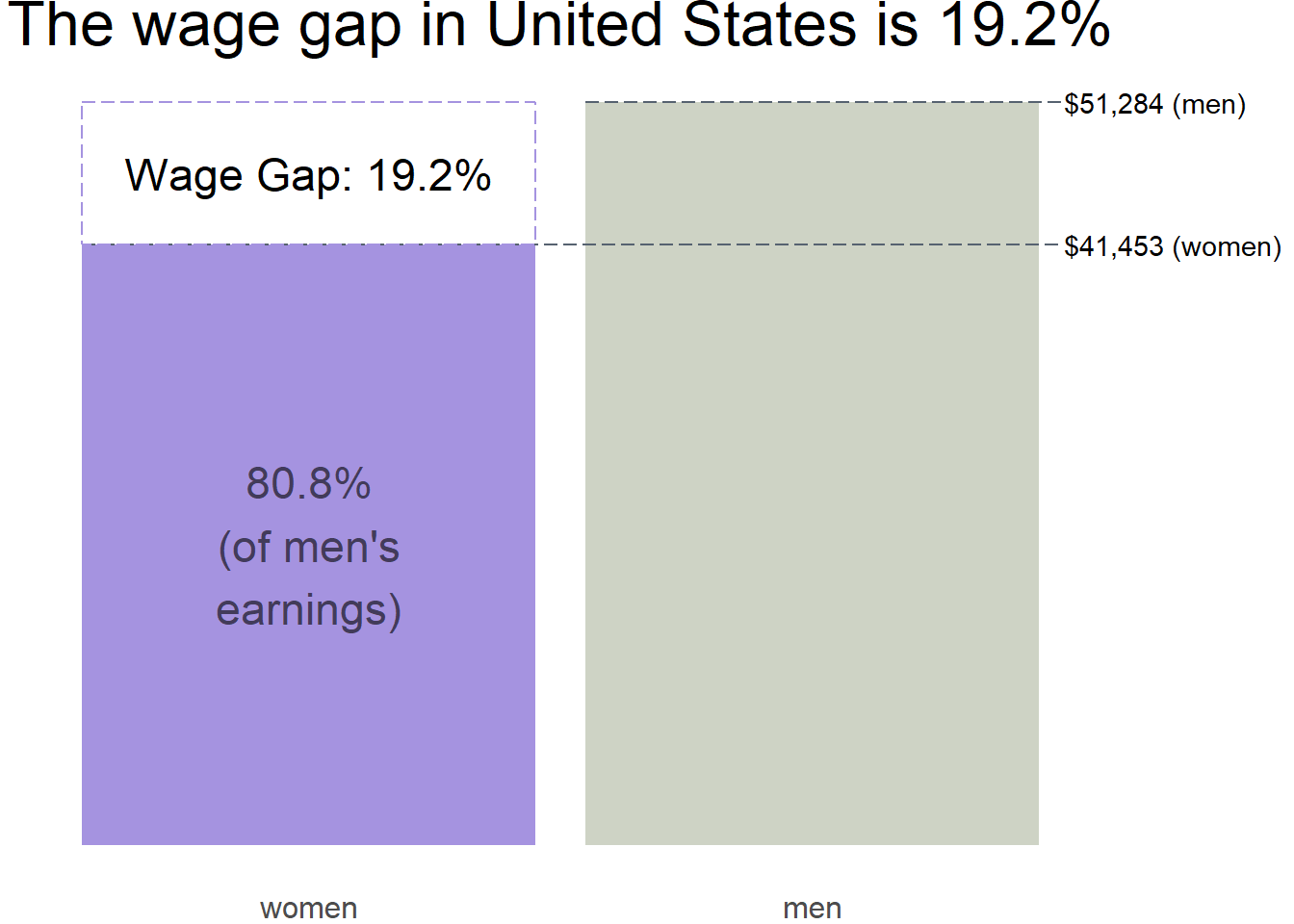
The wage gap is a comparison of women and men’s earnings using the following formula:
\(Wage\:Gap = (1 - \frac{women's\:earnings}{men's\:earnings}) * 100\%\)
A wage gap of 19.2% indicates that women earn 19.2% less than men. Sometimes this is stated as a wage gap of 19.2 cents. This is equivalent to stating that women in United States earn 80.8 cents on the dollar.
Research explains some of the gender wage gap. For example, women are more likely to work in lower paying occupations and industries than men. And even when women work in the same occupation as men, women still often earn less. Research also points to other factors that partially explain the wage gap such as women’s disproportionate childcare obligations but much of the difference between women and men’s earnings is still unexplained by observable distinctions in worker characteristics
Technical notes
- This calculation only compares the earnings of workers who work full time, year round. For more data on other groups of workers, see Women’s Earnings and the Gender Wage Gap. 2016. Women’s Bureau, US Department of Labor.
- The data used in this calculation comes from the American Community Survey at the US Census Bureau. They survey a subset of the population that is representative of the United States population.
For a comprehensive review of research on this topic, see Blau, Francine D, and Lawrence M Kahn. 2016. “The Gender Wage Gap: Extent, Trends, and Explanations.” Working Paper 21913. National Bureau of Economic Research.